Quote:
Originally posted by Mr. Duff

^What is that? I'm confused.  |
Here's a map of countries who use it followed by a description.

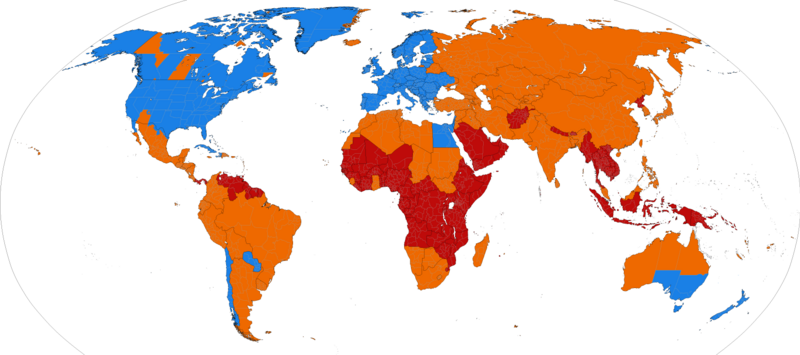
Key:
Blue = Uses Daylight Savings Time
Orange = Used to Use Daylight Savings Time, But No Longer Does
Red = Never Used Daylight Savings Time
Daylight savings time is the convention of advancing clocks so that afternoons have more daylight and mornings have less. Typically clocks are adjusted forward one hour near the start of spring and are adjusted backward in autumn. Modern DST was first proposed in 1907 by the English builder William Willett. Many countries have used it since then; details vary by location and change occasionally.
Benefits:
Delaying the nominal time of sunset and sunrise reduces the use of artificial light in the evening and increases it in the morning. As Franklin's 1784 satire pointed out, lighting costs are reduced if the evening reduction outweighs the morning increase, as in high-latitude summer when most people wake up well after sunrise. An early goal of DST was to reduce evening usage of incandescent lighting, formerly a primary use of electricity.
Retailers, sporting goods makers, and other businesses benefit from extra afternoon sunlight, as it induces customers to shop and to participate in outdoor afternoon sports.
In 1975 the U.S. DOT conservatively identified a 0.7% reduction in traffic fatalities during DST.
DST has mixed effects on health. In societies with fixed work schedules it provides more afternoon sunlight for outdoor exercise. It alters sunlight exposure; whether this is beneficial depends on one's location and daily schedule, as sunlight triggers vitamin D synthesis in the skin, but overexposure can lead to skin cancer.
Why Do We Do It?:
As the Daylight Saving Time category explains, moving our clocks an hour ahead means more sunlight later in the day. Aside from its obvious brightening effect, this act of time trickery also conserves energy. By "springing ahead," we shorten the peak period when electricity is needed to power lights, televisions, and other appliances before bedtime.
Benjamin Franklin was the first to suggest the idea in his essay, "An Economical Project." But William Willett is considered the originator of daylight savings. He started the campaign that led to "summer time," ratified in the U.K. in 1916. European countries adopted daylight saving time over the next two years, and the United States followed with an act in 1918, though the new system was practiced inconsistently.
In 1966, the U.S. Uniform Time Act established a set pattern for observing daylight saving time across the country. The act was revised in 1986, moving the start date a month earlier to the first Sunday of April. This saves an additional 300,000 barrels of oil each year.
Approximately 70 countries observe daylight saving time, but the start and end dates vary. And countries near the equator don't participate since their daylight hours change minimally throughout the year.